There are two types of transistor, NPN and PNP. Again, searching will describe these to you better than I can, however, for this I'm using an NPN (I discovered after allot of wasted time that a PNP doesn't work here!).
We are going to make a circuit which will flash an LED on and off, the LED is powered by a 9V battery and the current from this battery is controlled from a digital pin on the Netduino.
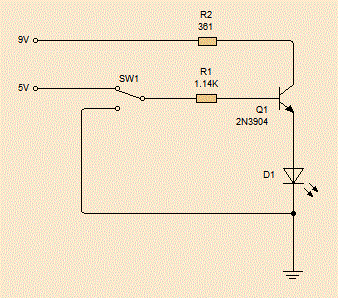
The circuit diagram is this:
 |
| Transistor Circuit |
The resistor R2 reduces the power so we don't blow up the LED, SW1 is the Netduino pin, switching between ground and 5V.
The operation is very simple, when SW1 is connected to ground, the resistance of Q1 is high enough for almost no current to flow, so the LED of off. When SW1 is connected to 5V, the resistance in Q1 plummets and allows enough current to flow to power the LED.
NB: A PNP transistor has a different symbol and doesn't work in this circuit, the resistance doesn't get high enough to turn off the LED.
Also, the resistor R1 is in place for two reasons, firstly, it only takes a small current lower the transistor's resistance as much as it will go. This is called saturating the resistor. Secondly, when the transistor changed from low to high or back a pulse of the full voltage and current might be briefly exposed to the Netduino and may damage it, the high resistor stops this pulse from being at a dangerous level.
No comments:
Post a Comment